Amino Acids: Building blocks of proteins.
B
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): Naturally occurring soil bacteria that occur worldwide and produce protein toxins specific to certain insects (e.g. moths, beetles, blackflies or mosquitoes).
Biotechnology: Biotechnology is the application of science and engineering in the direct or indirect use of living organisms, or parts, or products of living organisms in their natural or modified forms.
Bt corn technology: Bt corn has been modified to produce insecticidal proteins that are made by Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a naturally occurring soil bacterium.
C
Cross Resistance: resistance to a pesticide caused by exposure of a population to a different pesticide.
Cry Proteins: Any of several proteins that comprise the crystals found in spores of Bacillus thuringiensis. Activated by enzymes in an insect’s midgut, these proteins attack the cells lining the gut, cause gut paralysis and subsequently insect death.
D
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Double-stranded molecule, consisting of paired nucleotide units grouped into genes and associated regulatory sequences. These genes serve as blueprints for protein construction from amino-acid building blocks.
E
Event: Successful transformation of an organism by insertion of genetic material (DNA). Events vary in the composition of the genetic package inserted into the organism and the particular location of insertion into the host DNA.
Expression: Production of the desired trait (e.g. Cry protein) in a transgenic plant. Expression varies with the gene, its promoter, and its insertion point in the host DNA.
G
Gene: The basic unit of inheritance and diversity; a section of DNA that codes for a specific product (e.g. protein).
Genetic Diversity: The huge variety in DNA sequences found in different organisms, that is responsible for the wide variety of plants and animals in the world.
Genetic Marker: Sequence of DNA that can easily be identified and which therefore can be used as a reference point for mapping other genes.
Genetic Modification: Describes a series of techniques used to transfer genes from one organism to another or to alter the expression of an organism’s genes.
H
Heredity: The transfer of genetic information from parents to their offspring by reproduction (e.g. leaf shape).
High-Dose Strategy: An approach for minimizing the rapid selection for resistance to transgenic plants by using plants that produce Cry proteins at a concentration sufficient to kill all but the most resistant insects.
Host Plant Resistance: Ability of a plant to avoid insect attack, kill attacking insects or tolerate their damage.
I
Instar: The stage of an insect between successive molts. E.g. the first instar is the stage between hatching and the first molt.
Integrated Refuge: A proportion of refuge seed (lacking expression of Bt protein) is blended with Bt seed before planting.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A management approach that integrates multiple, complementary control tactics (e.g. biological control, crop rotation, host plant resistance, insecticides) to manage pests in an effective, environmentally sound manner. IPM involves using multiple tools to manage pests within a long-term strategy. IPM includes prevention, scouting, and treatment when necessary. Successful and sustainable insect pest control cannot be achieved using only one tool. IPM is also the foundation for preventing resistance development to pest control tools.
Insect Resistance Management: tactics implemented to delay evolution of resistance in pest populations
M
Marker Gene: A genetic flag or trait used to verify successful transformation, and to indirectly measure expression of inserted genes.
Mode-of-Action: Mechanism by which a toxin kills an insect. For example, the mode-of-action of Bt is ingestion and disruption of cells lining the midgut.
P
Promoter: A DNA sequence that regulates where, when, and to what degree an associated gene is expressed.
Protein: A molecule composed of many amino acids. There are many types of proteins with a wide range of functions.
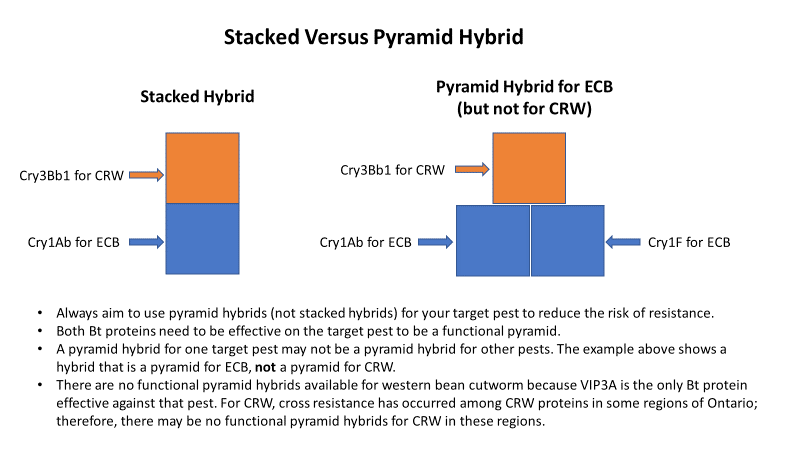
Pyramided hybrid: A hybrid that contains multiple, different modes of action against the same pest. Pyramided products are considered to delay the development of pest resistance, providing that resistance has not previously developed to one of the pyramided gene products.
R
Refuge: An area of corn planted without the Bt protein where susceptible pests can survive and produce a local population capable of inter-mating with any possible resistant survivors from Bt corn.
Resistance: Genetically based decrease in susceptibility to a control measure.
Resistance Management: A proactive process of limiting or delaying resistance development in a pest population with a focus on preserving susceptible genes.
RNA Interference (RNAi): A gene silencing process initiated by double-stranded ribo-nucleic acid (dsRNA).
S
Selection: A natural or artificial process that results in survival and better reproductive success of some individuals over others. Selection results in genetic shifts if survivors are more likely to have particular inherited traits.
Stacked hybrid: A hybrid that expresses multiple Bt traits/events that target different pests.
T
Transgenic Plant: A plant with one or more genes, genetic constructs, or traits that have been introduced from the same or a different species using recombinant DNA techniques.